
Explore the only 4-oil parenteral nutrition (PN) emulsion for pediatric patients1

One-of-a-kind blend of 4 oil sources1
Designed to nourish pediatric patients daily with a proprietary blend of 4 oils, SMOFlipid is the FIRST and ONLY 4-oil lipid injectable emulsion (ILE) with a well-established safety and tolerability profile.1 It has been administered to more than 7 million patients worldwide.*
*Data on file 4/1/25.

The same product you’ve trusted for adults is approved for children 17 and under who require PN
SMOFlipid is indicated in adult and pediatric patients, including term and preterm neonates, as a source of calories and essential fatty acids for parenteral nutrition (PN) when oral or enteral nutrition is not possible, insufficient, or contraindicated.1
SMOFlipid helps to nurture growth in pediatric patients1,4-6
- Infants receiving SMOFlipid experienced adequate growth.1
- Preterm infants receiving SMOFlipid experienced higher EPA and DHA levels compared to those receiving a soybean oil lipid emulsion.*4,5
- SMOFlipid is associated with a lower omega-6 to omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid ratio compared to soybean oil–based lipid emulsions in preterm neonates.5,6
- SMOFlipid has a well-established safety and tolerability profile.1
*Based on composition of the product.
Parenteral nutrition-associated cholestasis (PNAC) may develop less frequently in pediatric patients fed a 4-oil ILE vs 100% soybean oil (SO) ILE1
In a randomized clinical trial among neonates and infants expected to be treated with PN for at least 28 days, PNAC, a precursor to parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease (PNALD), developed less frequently in SMOFlipid-treated patients than in 100% SO lipid emulsion-treated patients.1
Pediatric Study 1 also compared the incidence of PNAC (DBIL >2 mg/dL with a second confirmed DBIL >2 mg/dL at least 7 days later) in both groups1:
- PNAC mostly occurred in patients who received treatment for more than 28 days
- 2.4% (2/83) of SMOFlipid-treated patients developed PNAC
- 11.5% (9/78) of SO lipid emulsion-treated patients developed PNAC
There was increasing uncertainty in the estimate of the cumulative incidence of PNAC as fewer patients were at risk.1
Parenteral Nutrition-Associated Liver Disease: Increased risk in patients who receive parenteral nutrition for greater than 2 weeks, especially preterm neonates. Monitor liver tests; if abnormalities occur, consider discontinuation or dosage reduction.1
Intravenous lipid use in high-risk neonates requiring PN and associated hepatic outcomes7
Study Purpose and Design:
- Evaluate effects of SMOFlipid vs. Intralipid® in neonates requiring PN ≥28 days
- Double-blind, randomized, controlled trial at 14 US study sites
- Randomization of 161 term and preterm neonates at high risk for IFALD
- Intervention: Intralipid (n=78), SMOFlipid (n=83), up to 3 g/kg/day as part of PN (mean lipid dose 2.0 ± 0.1 g/kg/day SMOFlipid, 2.6 ± 0.2 g/kg/day Intralipid)
Liver Results:
- Analysis showed a trend toward a lower risk of cholestasis in the SMOFlipid group (NS due to the low number of events)
- Significantly lower conjugated bilirubin concentration (P = 0.006) at the end of the initial treatment phase in the SMOFlipid group
- No new cases of confirmed cholestasis occurred after day 28 in the SMOFlipid group for up to 84 days
Study Limitations:
There was a low incidence of cholestasis in both treatment groups compared to historical data. Additionally, there was a low completion rate (40%) predominantly due to earlier weaning from PN. The use of SMOFlipid in patients with established cholestasis was not assessed.
“Our data supports use of [SMOFlipid] a composite ILE with EPA and DHA from fish oil, for PN in high-risk neonates and infants at risk of IFALD such as those with impaired intestinal function or surgical conditions preventing use of enteral nutrition.”
Consider SMOFlipid as an alternative to Intralipid in high-risk neonates.
Parenteral Nutrition-Associated Liver Disease: Increased risk in patients who receive parenteral nutrition for greater than 2 weeks, especially preterm neonates. Monitor liver tests; if abnormalities occur, consider discontinuation or dosage reduction.1
*This trial was funded by Fresenius Kabi Deutschland GmbH upon requirement of a postmarketing study from the United States Food and Drug Administration.
Abbreviations: DHA, docosahexaenoic acid; EPA, eicosapentaenoic acid; IFALD, intestinal failure-associated liver disease; ILE, lipid injectable emulsion; NS, not significant; PN, parenteral nutrition.
EPA and DHA (omega-3 fatty acids) are considered to be important for healthy development of infants due to their physiological roles8,9
![]()
May be considered conditionally essential for growth and development10,11
![]()
Important structural elements of cell membranes9
![]()
SMOFlipid contains 1‑3.5% of both EPA and DHA1
Explore the fatty acid pattern of SMOFlipid vs human breast milk12,13

In this analysis, SMOFlipid had a fatty acid composition that is similar to breast milk.12,13
Impact on bilirubin in SMOFlipid clinical trials5
Decrease in total bilirubin concentration
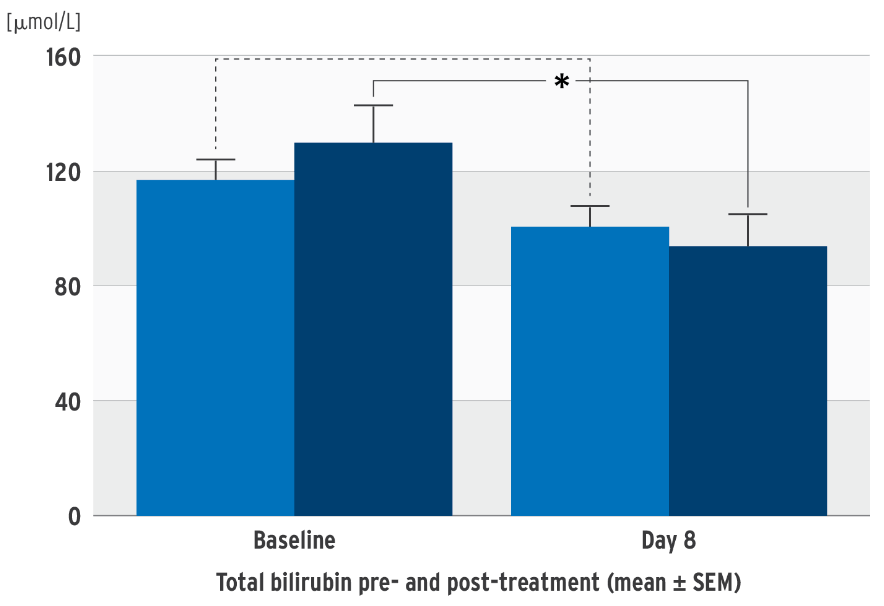
Change in direct bilirubin concentration
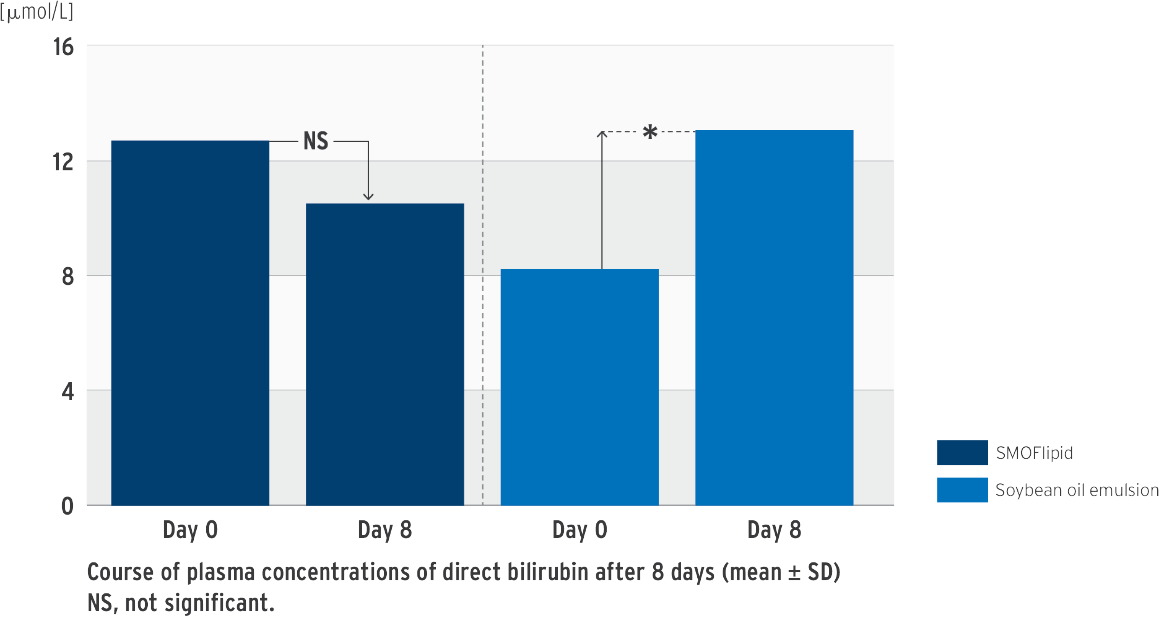
*P‹0.05 between group difference of changes from baseline to last visit
Prospective, randomized, controlled, double-blind trial in 53 neonates (‹ 34 weeks’ gestation); PN at least 7 days; test group: SMOFlipid, control group: soybean oil emulsion
concentration in the SMOFlipid group.
• One on-label submitted study showed no difference in total bilirubin between the two groups14

Appropriate daily dosing is vital
The dosing of SMOFlipid varies in pediatrics and neonates; each group has its own specific dosing specifications.1
- Protect the admixed PN solution from light
- Use a non-vented, non-DEHP 1.2 micron in-line filter set during administration
Recommended dosage depends on age, energy expenditure, clinical status, body weight, tolerance, ability to metabolize and eliminate lipids, and consideration of additional energy given to the patient.1
Do not exceed the maximum infusion rate of 0.75 mL/kg/hour in pediatric patients.1
| Age | Nutritional Requirements | Direct Infusion Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recommended Initial Dosage and Maximum Dosage | Initial | Maximum | |
| Birth to 2 years of age (including preterm and term neonates*) | Initial 0.5 to 1 g/kg/day not to exceed 3 g/kg/day** |
0.1 to 0.2 mL/kg/hour for the first 15 to 30 minutes; gradually increase to the required rate after 30 minutes | 0.75 mL/kg/hour |
| Pediatric patients 2 to <12 years of age | Initial 1 to 2 g/kg/day not to exceed 3 g/kg/day** |
0.2 to 0.4 mL/kg/hour for the first 15 to 30 minutes; gradually increase to the required rate after 30 minutes | 0.75 mL/kg/hour |
| Pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age | Initial 1 g/kg/day not to exceed 2.5 g/kg/day** |
0.2 to 0.4 mL/kg/hour for the first 15 to 30 minutes; gradually increase to the required rate after 30 minutes | 0.75 mL/kg/hour |
*The neonatal period is defined as including term, post-term, and preterm newborn infants. The neonatal period for term and post-term infants is the day of birth plus 27 days. For preterm infants, the neonatal period is defined as the day of birth through the expected age of delivery plus 27 days (i.e., 44 weeks post-menstrual age).
**Daily dosage should not exceed a maximum of 60% of total energy requirements.
SMOFlipid has a well-established safety and tolerability profile.1 It has been administered to more than 7 million patients worldwide.*
*Data on file 4/1/25.
SMOFlipid resources
Explore additional SMOFlipid materials by visiting our Resource Center.
For Consumers
SMOFLIPID® (lipid injectable emulsion USP), for intravenous use
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
What is SMOFlipid?
- Indicated in adult and pediatric patients as a source of calories and essential fatty acids for parenteral nutrition (PN) when oral or enteral nutrition is not possible, insufficient, or contraindicated.
- The hourly infusion rate in pediatrics should not exceed 0.75 mL/kg/hour and 0.5 mL/kg/hour in adults.
SMOFlipid should not be received by patients who have:
- A known allergy to fish, egg, soybean, or peanut, or to any of the active or inactive ingredients in SMOFlipid.
- Abnormally high levels of lipid (triglycerides) in the blood.
SMOFlipid may cause serious side effects including:
- Serious Adverse Reactions with Rapid Infusion of Intravenous Lipid Emulsion in Neonates and Infants: Strictly follow the recommended total daily dosage and do not exceed the maximum infusion rate. If poor clearance of fats occurs, the infusion should be stopped, and a medical evaluation started.
- Risk of Parenteral Nutrition-Associated Liver Disease: Parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease (PNALD) may progress to liver inflammation and damage caused by a buildup of fat in the liver with scarring and cirrhosis.
- Allergic Reactions: Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you are experiencing an allergic reaction.
- Fat Overload Syndrome, Refeeding Syndrome, Elevated Triglycerides (Hypertriglyceridemia): Your healthcare provider will monitor you for signs and symptoms of early infection and blood levels.
Monitoring/Laboratory Tests: The content of vitamin K may interfere with blood clotting activity of medications.
For Consumers
SMOFLIPID® (lipid injectable emulsion USP), for intravenous use
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
What is SMOFlipid?
- Indicated in adult and pediatric patients as a source of calories and essential fatty acids for parenteral nutrition (PN) when oral or enteral nutrition is not possible, insufficient, or contraindicated.
- The hourly infusion rate in pediatrics should not exceed 0.75 mL/kg/hour and 0.5 mL/kg/hour in adults.
SMOFlipid should not be received by patients who have:
- A known allergy to fish, egg, soybean, or peanut, or to any of the active or inactive ingredients in SMOFlipid.
- Abnormally high levels of lipid (triglycerides) in the blood.
SMOFlipid may cause serious side effects including:
- Serious Adverse Reactions with Rapid Infusion of Intravenous Lipid Emulsion in Neonates and Infants: Strictly follow the recommended total daily dosage and do not exceed the maximum infusion rate. If poor clearance of fats occurs, the infusion should be stopped, and a medical evaluation started.
- Risk of Parenteral Nutrition-Associated Liver Disease: Parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease (PNALD) may progress to liver inflammation and damage caused by a buildup of fat in the liver with scarring and cirrhosis.
- Allergic Reactions: Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you are experiencing an allergic reaction.
- Fat Overload Syndrome, Refeeding Syndrome, Elevated Triglycerides (Hypertriglyceridemia): Your healthcare provider will monitor you for signs and symptoms of early infection and blood levels.
Monitoring/Laboratory Tests: The content of vitamin K may interfere with blood clotting activity of medications.


